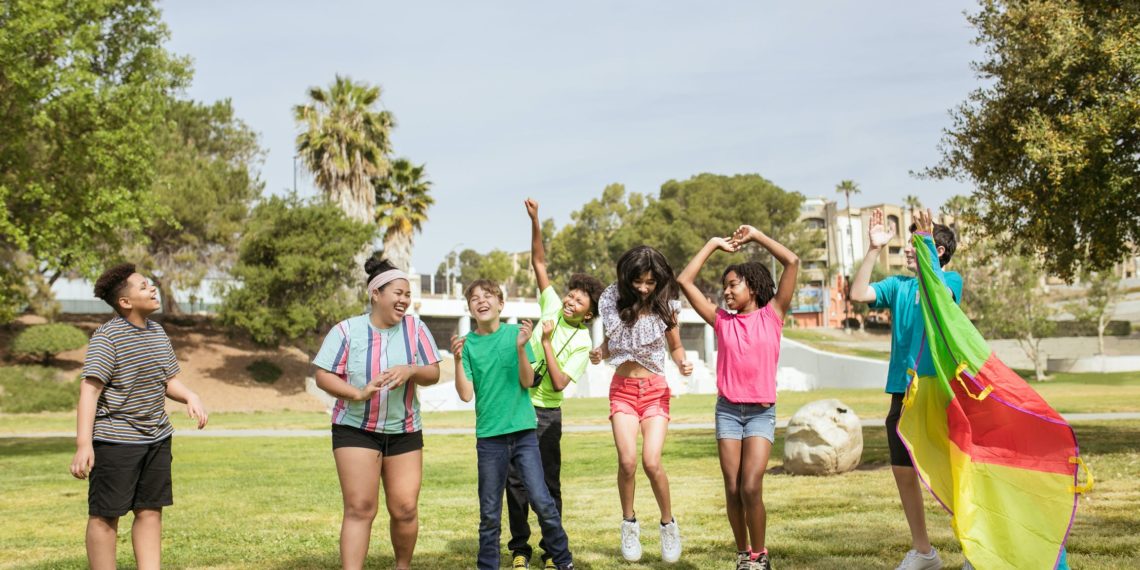
A community is a social group defined by location, occupation, lifestyle, situation, belief, or shared interests. The following are instances.
Sense of Place
The term “community” is most frequently used to refer to social interaction that takes place in a physical or digital space. For instance, the social interactions between neighbors or residents in the same town. This imparts character to a location and instills a sense of place in its inhabitants. As a result, designing cities and towns with appealing public areas foster a sense of community among residents.
Civility
In a community, members treat one another with respect and attempt to resolve differences in a fair manner consistent with the dominant culture’s norms.
Solidarity
The capacity of a community to identify common aims and values and to band together in pursuit of those goals and values.
Celebration
Communities find reasons to gather and celebrate life and culture.
Social Status
Social standing is earned esteem within a community. This varies significantly between communities. Whereas one culture may value conformity to standards or values, another may value uncontrolled uniqueness and coolness.
Communal Experience
Participating in fun activities as a group, such as recreation, risk-taking, and meaningful labor. Individuals who take few risks alone are frequently content to do so in the setting of a group.
Empathy
Members of a community might express sympathy and empathy for one another.
Chance Encounters
A community is a location where you may run across familiar faces or make new acquaintances. For instance, a community with a play street encourages neighbors to socialize and engage in recreational activities.
Socialization
Communities give a chance for interaction and the development of interpersonal skills within the framework of a culture. This enables the development of social skills and cultural capital.
Identity
A person’s community memberships may be viewed as an integral part of their identity.
Cosmopolitanism
A community can be founded on shared conceptions of identity. Alternatively, it might be founded on an appreciation of diversity. For instance, cosmopolitanism is the universal acceptance of culture and society based on similar interests or aspirations.
Membership
A community fosters a sense of belonging and social inclusion. A person may be a member of many communities depending on their neighborhood, city, career, hobbies, lifestyle, beliefs, circumstances, and other facets of their identity.
Participation
A community may provide activities, events, and initiatives to channel members’ energies.
Exchange of Information
A chance to interact with and learn from others. In many circumstances, a community plays a critical role in the generation and dissemination of domain-specific and contextual knowledge.
Influence
Two-way communication in which individuals have the potential to influence one another and the community’s thoughts.
Personal Satisfaction
Human needs such as social connectivity and a sense of purpose are met by communities.
Giving Opportunities to contribute to a cause you believe in. Individuals frequently feel a great urge to give back to the community that has benefitted them.
If you’re interested in learning more about society, culture, and norms, here’s an article on why social norms exist.

Social Media Manager
Karolyn leads our online team, ensuring we get the latest stories that need telling.